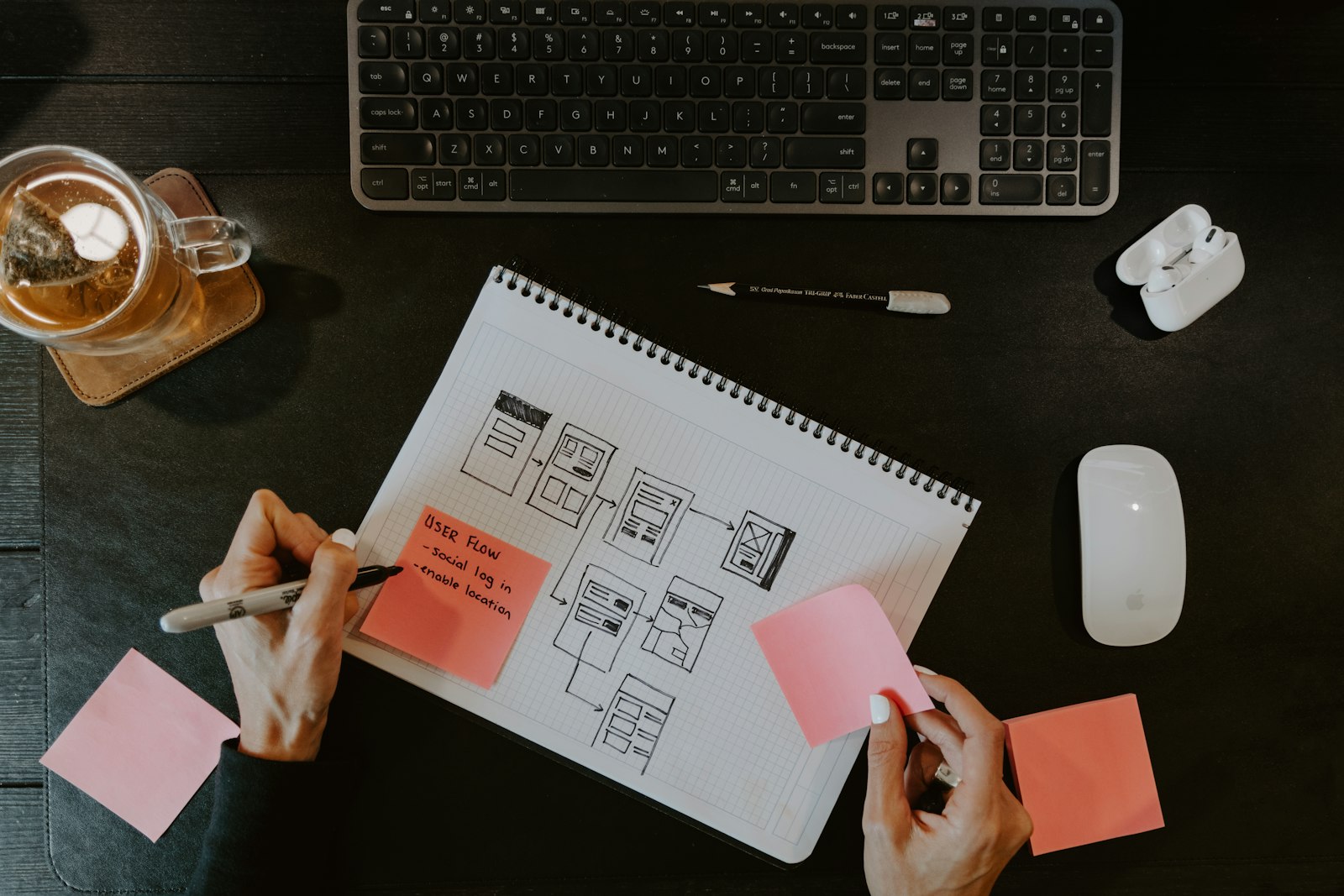
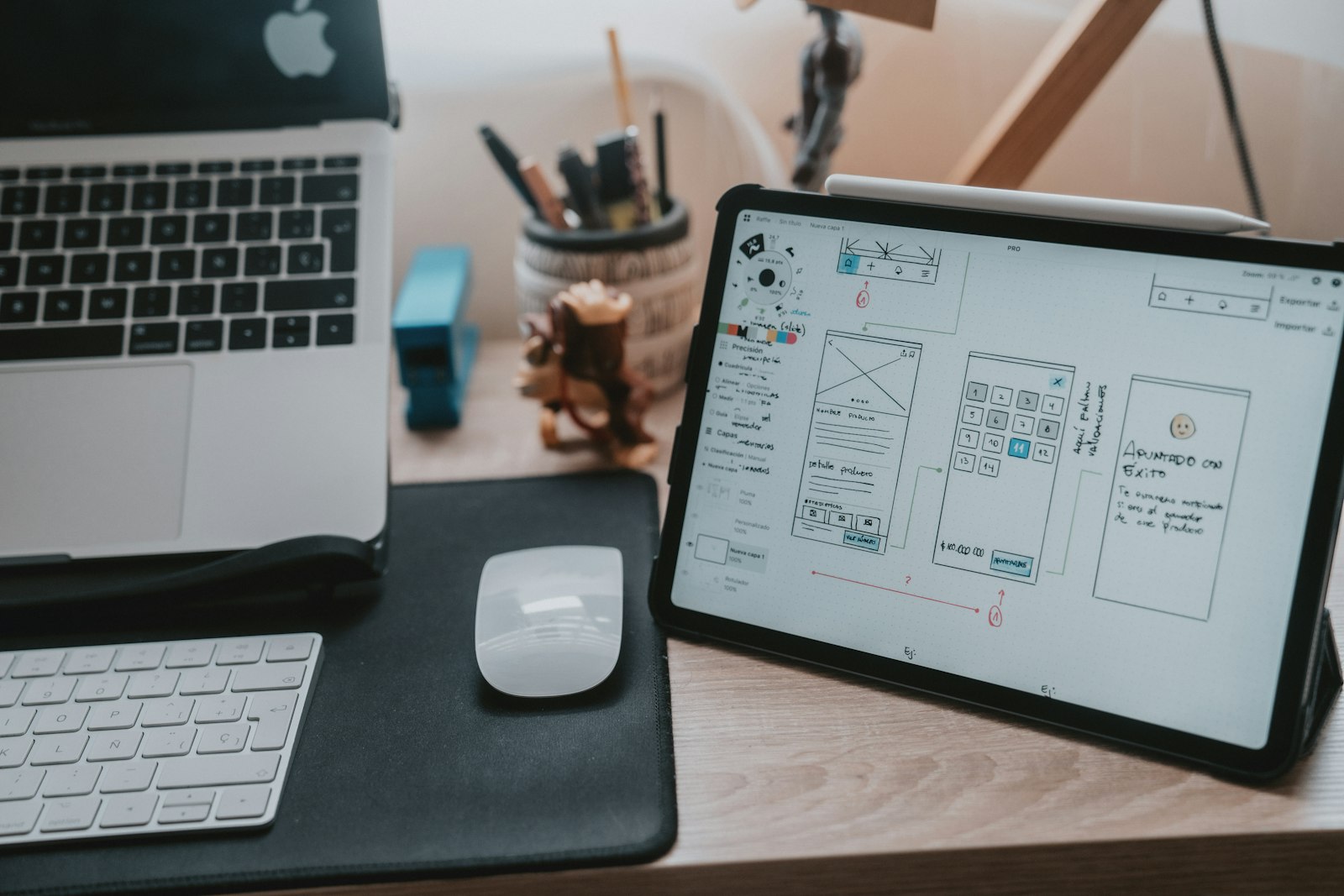
A UX designer is responsible for optimizing every interaction that an end-user has with their company. The term UX design, short for user experience design, refers to all aspects of interaction between humans and products. These experiences include branding, website design, navigating a mobile app, information architecture, product usability, interactive elements, etc.
UX design is associated primarily with digital experiences but can also apply to physical product design and its user interaction, like trying out a new shoe at the Nike store, or taking advantage of the irresistible Apple store experience to buy a new machine for UX design.
As a UX designer, you'll need to understand motivations to ensure that the 'user experience' for end users is efficient and pleasurable. You'll be involved in the aesthetics and design of products and services for customers.
Read on for an overview of the both technical and soft skills needed for a user experience design career.
Adjunctive Resources → Professional UX Design Courses for DesignOps Job roles
What Technical Skills Do You Need to Become a UX Designer?
UX designers perform vastly different types of work — a cluster of core activities and responsibilities — focusing on the all the important design related aspects of product development, including design, usability, function, testing and even marketing.
UX design is a major that can be incredibly easy to get into. To become a successful UX designer, you need to learn the essential technical skills to position yourself for success in the highly competitive job market.
You will benefit from mastering these applied skills.
Wireframing, UI Prototyping and Mockups
Wireframes are low-fidelity design sketches that represent different screens to map out each step a user takes when using a product or service. This is an essential part of the product development process to provide a visual understanding of what the different stages of the product will look like throughout the user journey.
A wireframe is an early visual that can be used to review with the client to establish the structure and flow of conceivable design solutions. Establishing the basic structure helps to spot constraints and opportunities to bridge the gap between abstract requirements and practical solutions.
Image by Kelly Sikkema on Unsplash
Wireframing is not prototyping, and prototypes are not mockups.
Wireframing is exceedingly valuable in the interaction design process to examine how concepts accommodate end-user and business needs. From a practical perspective, the wireframes become the primary tools for collaboration toward UI prototyping and creative process.
UI Prototyping is the phase where you’re hashing out ideas — and these ideas are to be grounded in your research, with a laser-sharp focus on designing for business objectives. It involves thorough usability testing of the wireframes and validating ideas before passing the final designs to the responsible stakeholders for the development process.
Mockup is then a realistic visual model that includes more stylistic and visual UI details of what a final webpage or application will look like.
Wireframing and UI prototyping are critical UX skills to demonstrate your UX acumen. You can start with a pen and paper to sketch out wireframes and user flows for an app or website you often use to get familiar with the components to understand your own behaviour, needs, and even motivation.
If you’re just getting started, learn with some popular wireframing and prototyping tools, like UXPin, InVision, Sketch, or Adobe XD. Here are a few of the best resources to learn about the elements of interaction design. These resources will cover skills like wireframing, prototyping, user research, usability testing, and design softwares.
- UI/UX Design Classes ← Skillshare
- UX Designer Nanodegree ← Taught by UX Industry Experts with emphasis on Portfolio Design and Job assistance.
UX Research and Testing
UX designers are researchers and this skill is so critical that most companies have a specialized role in the DesignOps known as the UX researcher.
UX design entails research like demographic, economic, and product research are major components of designing for experience. Therefore, you must learn how to investigate methods and conduct research in order to understand the target audience, and how to translate your findings into product designs with context and insights.
UX designers borrow design research techniques from the academics, market researchers, UX data scientists and others. Among the research methods, UX designers gather data and insights about the target audience and synthesize that data to improve usability. The primary goal of data-driven design research is to inform the design process from the mindset of the end-user. This process involves usability testing that helps prevent us from designing for ourselves.
Image by UX Indonesia on Unsplash
If you are just starting your journey into UX design, don’t worry too much about the nuances of UX Research for now. UX Research is technical, but it’s ok if you’re just following the pattern and instructions employed by other designers. Here are a few of the best resources we’ve found for learning fundamental concepts imperative to UX Research and usability testing.
UX Writing
UX writing is like an artistic discipline with an emphasis on aesthetics and creative freedom to complement design's usability with texts that appear throughout the interface of digital products (websites, applications, etc.).
As the Internet is becoming progressively advanced with complex technologies, trends and global user experience, the need for clarity also grows to provide a fluid visual experience. Therefore, UX designers must conduct a through UX research to deliver the right message about their products and services from the inside out—everything from home screen, product pages, sales flow and contact information, to button copy and push notifications.
Image by Amélie Mourichon on Unsplash
Companies interviewing for the UX roles are always looking for designers who can defend their judgments for the initiatives they take, including but not limited to why they’ve chosen a particular word for a label and other word choices. For this reason, they must possess exceptional UX research abilities to explain why a particular word or a statement is a far better choice than another.
UX designers define their own role responsibilities by taking on cross-functional tasks like generating a wireframe, developing guidelines, drafting editorial strategies, etc. UX designers are storytellers and are naturally good at anticipating what words are lacking, and when.
Here are a few sources for aspiring UX designers, not only to learn more about the practice but also to evangelize to others.
- Introduction to UX Writing (Microcopy) ← Skillshare
Visual Communication Design
UX design professionals create and manage the production of visual design to inform, educate, persuade, and even excite end-users.
End-users are guided by the visual cues and learning how to combine visual arts and technology to communicate ideas will have a measurable effect on your design. Learning good visual communication, like making elements look clickable, forming visual hierarchy, using typography and color theory, including user controls to your advantage to limit the need for instruction manuals, are all critical skills for UX designers to have.
Image by Alvaro Reyes on Unsplash
UX designers use visual design software, like Figma, Frame, Sketch, InDesign, Illustrator and Photoshop, to create the visual elements of products and services. Besides proficiency in these applications, build the knowledge of the best visual design practices for things like typography, color theory, layout, movement, icons, etc.
UX designers have a highly specialized view of the design elements and improving your visual communication skills as a novice often means learning first graphic designing, typography, photography, logo design, and more.
Here are some of the best resources on the internet to learn to visual communication design.
- Graphic Design by David Carson ← Highly recommended MasterClass
Information Architecture – IA
Information architecture in UX design is organizing and structuring content in a way that is coherent.
UX designers make the journey easy for end-users to understand where they are, where they need to go, and what’s next. This requires an understanding of the visual hierarchy to deprioritize information to design interactive UI elements to induce people to take actions that bootstrap conversion through call-to-action elements both on web and mobile.
IA is intertwined with UX research and usability testing because investigating what end-users need and want is crucial for creating an effective information architecture design. This helps users find the information they’re looking for or complete their task with ease.
Image by Daniel Korpai on Unsplash
Hierarchy and navigation are important components of IA. The first establishes the structure of content, including sizes, while the second spells out how end-users will move through it. This discipline (IA) establishes the balance and helps organize the information in a way that meets the user’s needs and also business requirements.
The most basic example of information architecture is a sitemap.
https://kanger.dev/sitemap.xml
Learning the basic principles of information architecture in the context of user-centered design is essential for every ambitious UX designer who wants to pursue a DesignOps career. This skill is also important that most companies have a specialized role on their UX design team, known as the UX Architect.
- Intro to Information Architecture ← Skillshare
- Introduction to Information Architecture ← Pluralsight
UX Responsive Design
UX designers are not expected to write code or develop applications—that’s a task for web developers—it helps, however, to understand application development process and possess a basic knowledge of HTML, CSS and JavaScript or P5.Js.
Responsive design entails designing websites/applications that adapt to all devices, platforms, media queries, and screen sizes in terms of both form and function.
This is very critical as approximately 59% of the website traffic worldwide is generated by the mobile phones. Therefore, the design and development should respond to the end-user's behaviour and environment based on the platform, display aspect ratio and orientation.
Gif by Echovme
UX designers should have a high-level familiarity with the concept of responsive design to ensure that designs display differently across different screens. To set the ball rolling in your DesignOps career path, you can start by knowing the basic skills of responsive web design.
Responsive web design is primarily about offering a seamless user experience on any device and you can learn how to create a responsive website from start to finish, wireframing, iterating through the sitemap until the final stage.
Having basic coding skills will go a long way in helping you complete your projects and ease the transition between design-developer handoff.
- Responsive Web Design Essentials ← Skillshare
- Introduction to Responsive Web Design ← freeCodeCamp
UX Analytics
UX designers are expected to develop a deeper understanding of how their users interact with websites, mobile apps, digital products, and services.
We can update quickly Web and mobile apps design to accommodate the requirements of end-users. But how do you figure out what those needs are or even understand how those needs are changing? The short answer is UX analytics.
Like data analysts and marketing researchers, UX designers depend on analytics tools to examine user data to improve user experience. This also allows UX designers to identify bugs, design glitches, reduce customer friction, optimize sales funnels, reduce noise, etc.
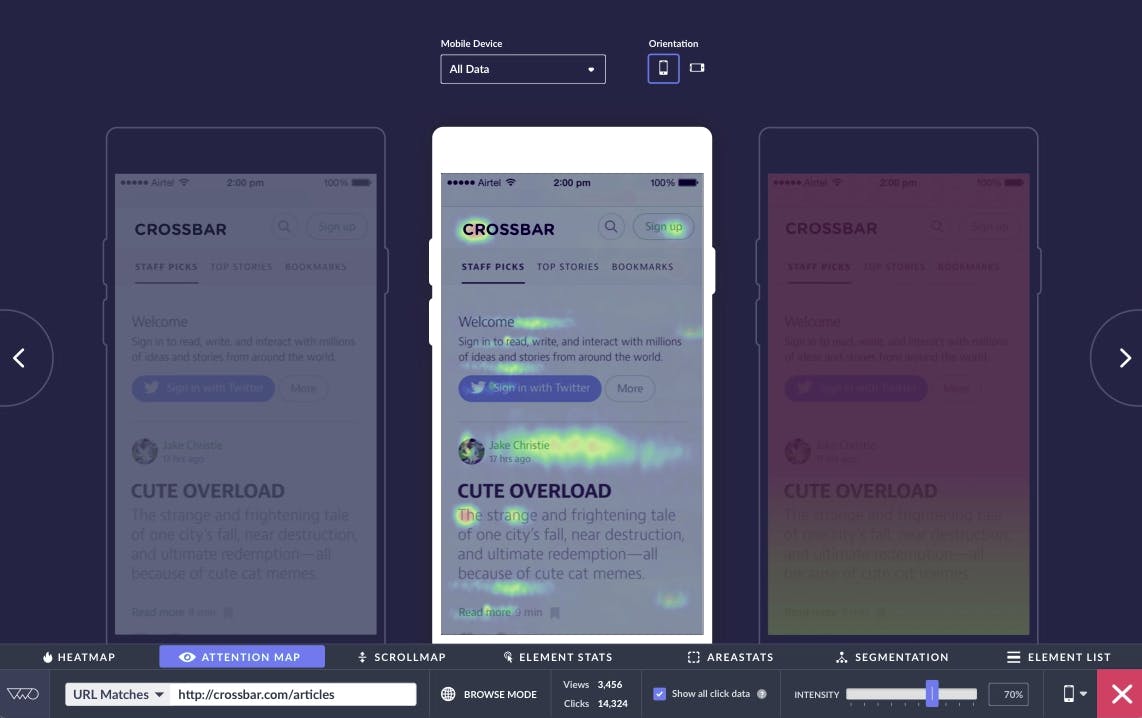
Image by Crossbar
UX designers need to be very knowledgeable about applying the analytical information to iterate quality designs, backed up by real numbers. After all, understanding interaction is difficult, but you can leverage insights from data to make design recommendations.
UX analytics helps to understand user's journey, such as session history, heatmaps, conversion rate calculator, user flow maps, user segmentation, web metrics, events, real-time analytics, etc.
This skill is a critical that some companies have a specialized role on their UX team known as the UX Data Scientist. While you don’t need to know every detail of UX data analysis but you can strengthen your resume by knowing the basics.
What Soft Skills Do You Need to Become a UX Designer?
In addition to mastering technical skills, UX designers must possess soft skills and aptitudes applied to serve the business side of UX design to manage relationships and streamline a design process that comprises multiple work settings.
Agile Project Management
As a UX designer, you must possess the ability to lead, coordinate, and stay on schedule to support the efficient product development process for all stakeholders.
You don’t need to know every detail of project management to be a successful UX designer, as you aren’t individually responsible for the product’s development.
You can enhance your resume by knowing the basics.
Critical Thinking
Critical Thinking is conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, examining and synthesizing information gathered from reliable sources as a guide to belief and action.
UX designers must be able to question all assumptions, understand their your own thought processes, and develop superior foresight to make empirically based design recommendations.
All UX designers know the importance of asking the questions, including dumb ones, during user research, interviews, and testing.
Curiosity
UX designers who are curious can engage with clients, products, and challenges in purposeful ways.
Curiosity leads through the insightful journey of thinking clearly to engage more deeply with problems to provide solutions.
UX is a changing field and designers must be curious to keep up.
Empathy
Empathy is the ability to realize the emotions of others. UX emphasizes a positive customer experience. That’s why the best UX designers conduct a thorough research to learn about their target audience and their inclinations.
Empathy allows UX designers to create products that truly engage and delight.
Communication and collaboration
Strong communication skills help UX designers to create, collaborate, adapt, and improve products with ease. Therefore, communication and collaboration are essential in UX design.
You must possess the ability to convey product ideas, explain your thoughts behind design inspirations, and collaboration with other teams.
The work of UX designers requires elements of storytelling.
Conclusion
As a UX designer, you ought to be both self-directed and collaborative, but you must be creative. Creativity and attention to detail are keys to success in this position.
Thanks for making it to the end....
kanger.dev is supported by our audience. We may earn affiliate commissions from buying links on this site.